The Lifespan of Different Roofing Materials: What to Expect
The material selected is one of the most critical aspects to bear in mind with regard to roofing. In addition to influencing the aesthetic appeal of your home, the material of its roof has a substantial impact on its longevity and durability. Every roofing material is distinguished by its unique set of qualities and its own specific lifespan.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the lifecycle of different roofing materials, enabling readers to make well-informed decisions regarding roof installation or replacement.
Pavement Shingles:
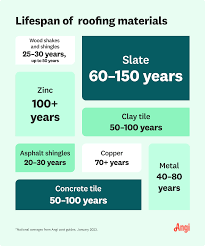
- Between 15 and 30 years of age
- Asphalt shingles are widely utilized in roofing construction owing to their cost-effectiveness. Nevertheless, their durability may fluctuate as a result of climate, upkeep, and shingle quality.
Shakes and Shingles of Wood:
- Between 20 and 25 years of age
- Shakes and shingles made of wood are renowned for their inherent attractiveness. Proper maintenance can extend their lifecycle, but they are prone to rot and decay in moist environments.
The Metal Roof:
- Between 40 and 70 years of age
- Steel or aluminum metal roofs are exceptionally resilient and long-lasting. Their resistance to severe weather conditions and low maintenance requirements are noteworthy.
Slate Cladding:
- More than fifty to one hundred years
- Slate is an exceptionally rugged and aesthetically pleasing roofing material. If installed and maintained properly, this costly material can last for at least a century.
Concrete or Clay Tiles:
- More than fifty years
- Tiles made of clay and concrete are renowned for their durability and visual attractiveness. Their resistance to insects and fire renders them a resilient option.
Synthetic or Composite Roofing:
- Between 30 and 50 years of age
- Composite roofing materials emulate the visual qualities of slate, wood, and other organic substances. They are more resilient and have a longer lifespan than wood.
EPDM Rubber Roofing:
- Between 20 and 30 years of age
- EPDM rubber roofs (ethylene propylene diene monomer) are frequently applied to low-slope or level roofs. They provide adequate durability and are reasonably priced.
BUR: Built-Up Roofing
- Between 20 and 30 years of age
- BUR roofs are composed of bitumen and reinforcing fabric applied in multiple layers. While they are resilient, consistent maintenance is necessary to extend their useful life.
Plastic and TPO Roofing:
- Between 20 and 30 years of age
- For commercial structures, thermoplastic olefin (TPO) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) roofing materials are prevalent. They provide excellent energy efficiency and durability.
Living or Green Roofing:
- Between 30 and 50 years of age
- Maintaining green roofs, which are vegetated, can extend their lifespan by several decades. Insulation and environmental benefits are provided by them.
Influencing Factors of Roof Lifespan:
- Extreme Weather Conditions: Including heavy snowfall, hail, heavy rain, or intense heat, can shorten the longevity of your roof. In general, materials that possess resistance to these elements exhibit an extended lifespan.
- Routine Maintenance and Inspections: Can help prolong the life of a roof. It is critical to address issues such as damaged shingles and leakage without delay.
- Installation Quality: Installation must be performed correctly by seasoned professionals such as https://rooftechconstruction.com/. Inadequate installation can substantially shorten the lifespan of a roof.
- Proper attic Ventilation: Is essential for maintaining stable temperature and moisture conditions within the roof, thereby mitigating the risk of untimely deterioration.
- Roof Pitch: In general, steeper roofs are more effective at shedding snow and precipitation, which can prolong the life of the roofing material.
- Material Quality: A substantial factor is the quality of the roofing material itself. In general, superior quality materials exhibit an extended lifespan.
- Extended Exposure to Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Emitted by the sun can induce deterioration in roofing materials as time passes. Materials resistant to UV rays have a prolonged lifespan.
- Tree Debris: Desiccated branches and leaf fall can inflict harm and facilitate the proliferation of lichen or algae, which may have an adverse effect on the durability of the roof.
In summary, it is critical to comprehend the longevity of various roofing materials in order to make well-informed decisions regarding one’s roofing requirements. Conditions such as climate, upkeep, and the grade of the materials utilized all influence the lifespan of a roof. Consistent maintenance and prompt repairs can effectively extend the life of your roof, thereby guaranteeing lasting protection for your residence. Consult a professional roofing companies Granger prior to installing a new roof or replacing an existing one in order to determine which material is optimal for your building’s location and requirements.